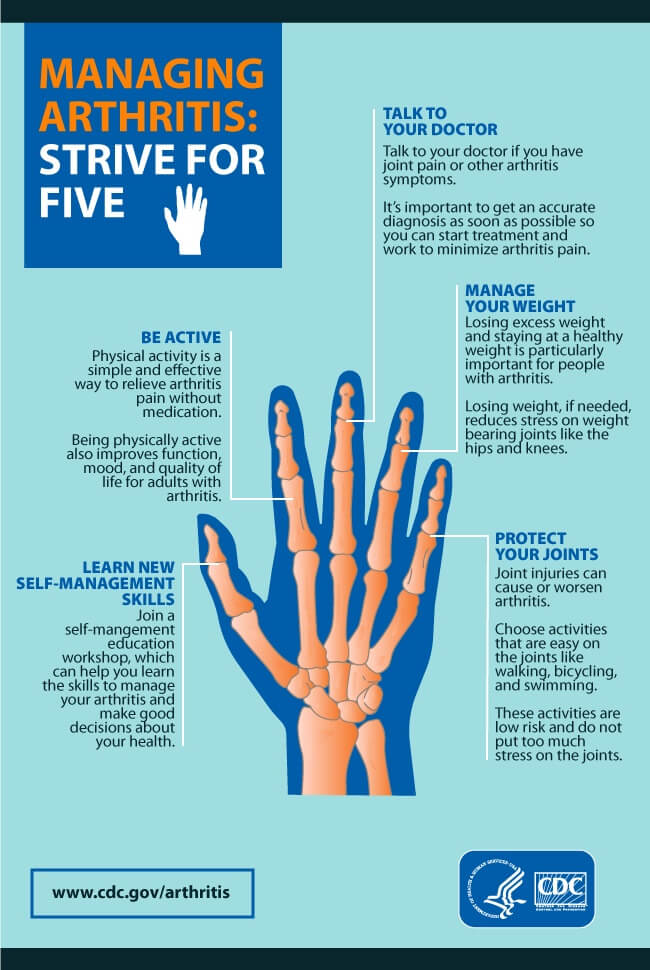
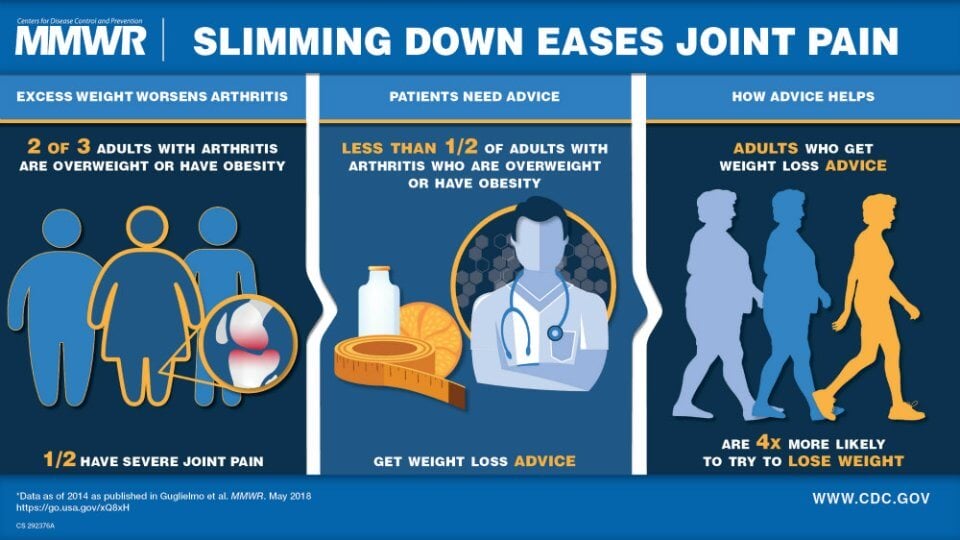
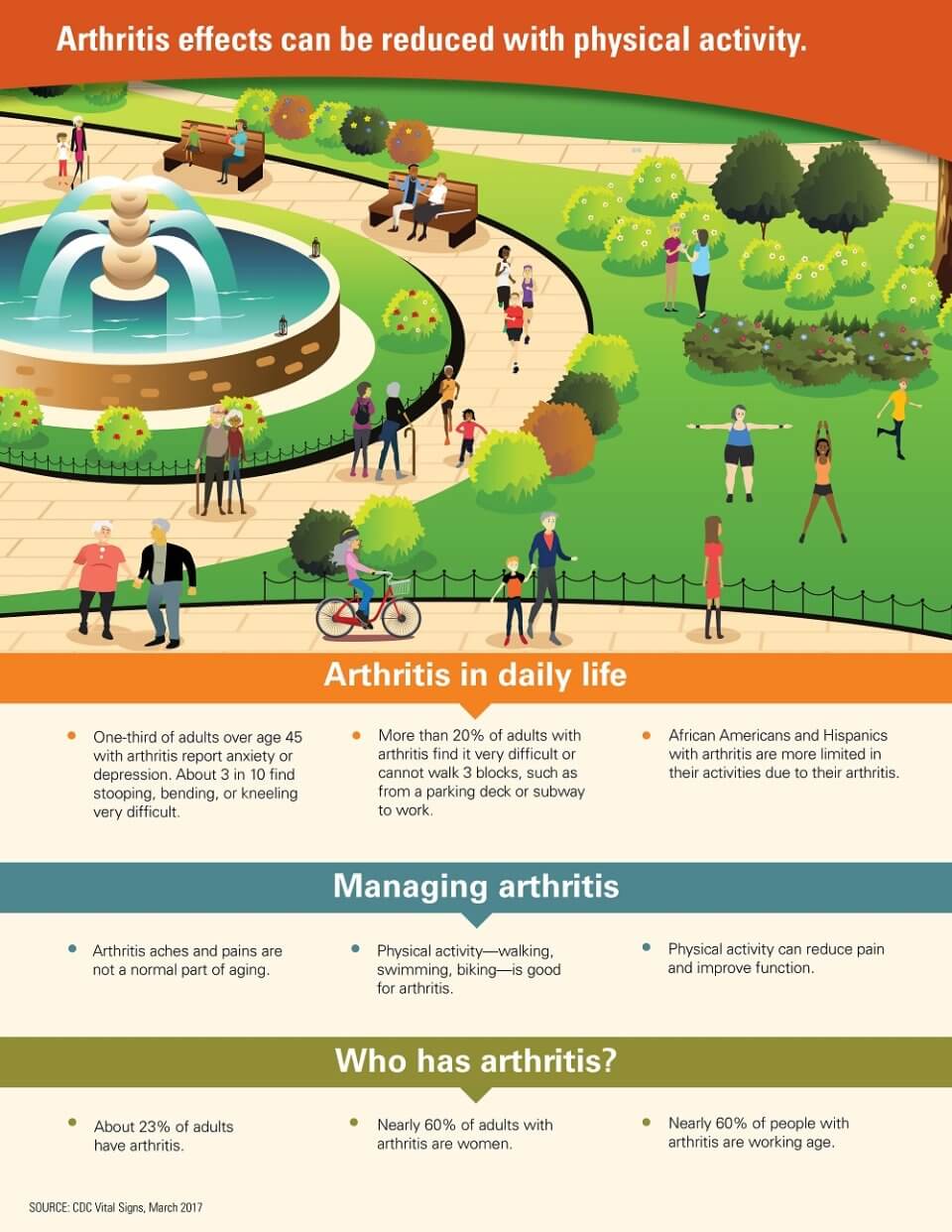
Anti-Inflammatory Diet – keep pain at bay!
An anti-inflammatory diet focuses on incorporating nutrient-rich, whole foods that help reduce inflammation in the body. It is important to include plenty of fibre, antioxidants, and omega-3s in the diet to promote overall health and wellness.
Fibre can be found in foods such as vegetables, whole fruits, and whole grains, which can help regulate digestion and reduce inflammation in the body. Antioxidants, found in colorful fruits and vegetables, help combat oxidative stress and reduce inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, also help to lower inflammation in the body.
To follow an anti-inflammatory diet, focus on eating whole foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, and fatty fish. These foods are rich in essential nutrients and can help reduce inflammation in the body. Eating a diverse range of nutritious foods can improve overall health and lower the risk of chronic inflammatory diseases.
Consume a variety of fruits and vegetables in your diet.
Eating colorful fruits and vegetables like oranges, bell peppers, pumpkins, tangerines, and papayas can reduce body inflammation. Carotenoids are antioxidants known for their anti-inflammatory properties, which can contribute to better overall health.
A small study from Sweden found that a Mediterranean diet, which includes lots of fruits and vegetables, can help reduce inflammation and improve joint function. The diet usually consists of a wide range of vibrant fruits and vegetables, wholesome grains, lean proteins, and nourishing fats. These elements synergistically combat inflammation and enhance joint wellbeing.
Nightshade vegetables like tomatoes, potatoes, peppers, and eggplant do not cause arthritis and eliminating them from your diet will not cure the condition. Eliminating nightshade vegetables from your diet will not provide significant relief for arthritis symptoms, despite individual sensitivities to certain foods. In fact, these vegetables are rich in nutrients and can be part of a healthy, balanced diet.
Eating a mix of fruits and vegetables rich in carotenoids, as part of a Mediterranean diet, can reduce inflammation and enhance joint function. Focus on overall dietary patterns rather than believing unfounded myths about certain foods causing or curing inflammation and arthritis.

Consider trying a small portion of nuts or seeds.
Adding a handful of nuts or seeds to your daily diet can provide a significant boost of essential nutrients. By adding walnuts, pine nuts, pistachios, and almonds to your meals, you can get calcium, magnesium, zinc, vitamin E, and fiber.These nutrients are crucial for bone health, heart health, immune function, and digestion.
You can enhance the benefits of nuts and seeds by adding them to salads, yogurt, or oatmeal. You can also enjoy them as a snack. You can also use them in smoothies or add them to your baked goods.These nuts and seeds are rich in ALA, a nutrient that supports heart health and the immune system. Including them in your meals and snacks will ensure you get vital nutrients..
Eating nuts or seeds daily can increase your intake of calcium, magnesium, vitamin E, and fiber. You can snack on walnuts, sprinkle pine nuts on pasta, or add almonds to oatmeal.
Add olive oil to your dish.
Olive oil has been hailed for its numerous health benefits, particularly for managing arthritis symptoms. It contains powerful anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce joint pain and swelling. Olive oil helps the body clean out damaged cells and generate new ones, which can be good for managing arthritis.
When choosing olive oil, look for extra virgin olive oil in dark bottles with a certification or seal for optimal freshness and quality. Additionally, the harvest date should be close to the purchase date to ensure the oil’s freshness and potency.
Incorporating olive oil into diet patterns, such as the Mediterranean diet, can have positive effects on managing arthritis symptoms. Studies have shown that the Mediterranean diet, which is rich in olive oil, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help reduce pain and improve physical function for people with rheumatoid arthritis.
In conclusion, including olive oil in the diet can have significant benefits for managing arthritis symptoms, thanks to its anti-inflammatory properties and ability to promote autophagy. This makes it a valuable addition to a healthy diet, particularly for those looking to alleviate arthritis symptoms.
Increase your fiber intake.
Adding more fiber to your diet is incredibly important for maintaining good health. Fiber has been linked to a variety of health benefits, including reducing inflammation and lowering the risk of heart disease and strokes.
Fruits, vegetables, wholegrain bread and cereals, whole wheat pasta, brown rice, and quinoa are all excellent sources of fiber that can easily be incorporated into your meals.
Studies have shown that fiber may also be linked to lowered levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) in the blood. CRP is a marker for inflammation in the body, and high levels have been associated with an increased risk of heart disease and stroke. By consuming more fiber-rich foods, individuals may be able to lower their CRP levels and potentially reduce their risk of inflammatory-related conditions, such as arthritis or cardiovascular diseases.
Therefore, adding more fiber to your diet through a variety of fruits and vegetables can help to address inflammation and decrease the risk of heart disease and strokes.
Berries are good
Some types of berries that are high in antioxidants and have been shown to reduce inflammation and improve symptoms of arthritis include strawberries, blackberries, and blueberries.
Strawberries are rich in vitamin C, which helps to reduce inflammation and joint pain associated with arthritis. They also contain anthocyanins, which are antioxidants that help to combat inflammation in the body.
Blackberries are also high in antioxidants and have been shown to reduce inflammation, making them beneficial for individuals with arthritis. They are also a good source of fiber, which can help to support overall joint health.
Blueberries are known for their high levels of antioxidants, particularly flavonoids, which have been found to decrease inflammation and improve symptoms of arthritis. They also contain vitamin K, which plays a role in bone health and may help to reduce the risk of osteoarthritis.
Incorporating these berries into a balanced diet can provide a natural way to help reduce inflammation and manage arthritis symptoms.
Green Tea will help
Green tea offers numerous health benefits, thanks to its high levels of polyphenols and antioxidants. These compounds have been shown to reduce inflammation and protect against cartilage damage, making green tea a great addition to a healthy diet. Incorporating green tea into your daily routine, aiming for at least two servings a day, can support overall health and wellness.
When choosing green tea, opting for the natural decaffeinated variety can be beneficial for those sensitive to caffeine. Additionally, using tea bags instead of powdered tea mixes ensures that you are getting the maximum benefits from the tea leaves.
Regular consumption of green tea has been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases, improved brain function, and increased fat burning. With its potential to lower inflammation and protect cartilage, green tea can also be beneficial for those with joint or arthritis-related issues. By making green tea a part of your daily routine, you can take advantage of its many health benefits and support your overall well-being.
Reducing inflammation and preventing damage
A balanced eating plan is essential for preventing joint damage and reducing inflammation in the body. Including a variety of fruits, vegetables, and lean protein sources provides the body with essential nutrients to support joint health. Consuming foods rich in antioxidants such as vitamins A, C, and E is also crucial for reducing inflammation and protecting the joints from damage.
Specific foods known to reduce inflammation include:
– Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are rich in antioxidants and have anti-inflammatory properties.
– Fatty fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to reduce inflammation in the body.
– Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are packed with vitamins and minerals that help reduce inflammation.
– Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds are good sources of anti-inflammatory fats and antioxidants.
By incorporating these nutritious foods into your diet, you can support joint health, reduce inflammation, and prevent damage. It’s important to follow a balanced eating plan that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods to support overall health and well-being.
Choosing the right diet
The key components of the Mediterranean diet include high consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins like fish and poultry, healthy fats from olive oil, nuts, and seeds, and moderate intake of dairy products. The DASH diet focuses on similar principles, with an emphasis on reducing sodium intake and increasing foods rich in potassium, calcium, and magnesium. Both diets are rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, which can help reduce inflammation in the body.
The Alternative Healthy Eating Index (AHEI) is a tool used to assess diet quality and measure adherence to healthy dietary guidelines. It focuses on key components such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and legumes, and limits intake of red and processed meats, sugary drinks, and sodium. By following the AHEI guidelines, individuals can achieve a similar healthy eating pattern to the Mediterranean and DASH diets.
Personalizing an anti-inflammatory diet to suit individual lifestyle and tastes can involve mixing and matching elements from different diets. For example, one can incorporate the Mediterranean emphasis on olive oil and fish, the DASH focus on reducing sodium, and the AHEI guidelines for overall healthy eating. By combining these elements, individuals can create a personalized anti-inflammatory diet that meets their specific needs.
In conclusion
A diet rich in certain foods and nutrients has been found to relieve inflammation and arthritis symptoms. Healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts, have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce joint pain and stiffness. Fatty fish, like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to decrease inflammation and improve symptoms of arthritis.
In addition, a diet rich in produce, such as fruits and vegetables, provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can help reduce inflammation and support overall joint health. Foods like berries, spinach, and kale are particularly beneficial due to their high levels of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds.
Overall, incorporating these foods into a well-balanced diet can help alleviate inflammation and reduce arthritis symptoms. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to receive personalized dietary recommendations for managing arthritis and inflammation.
























